How to use our load calculator
You don't have to be a math expert to use our load calculator.
This guide will help you get started so you can calculate what dimensions you need for your project.
NB: Please note that the result of the strength calculation only applies to the selected profile. When dimensioning structures with different profiles, strength calculation must be performed for the entire structure.
Make good choices for your project
Our load calculator is designed to give you the information you need to make a good choice when it comes to sizing your project.
The calculator allows you to test all of our structural profiles in a variety of different usage scenarios.
You choose the profile dimensions and the load conditions you want to take into account.

Understanding the load calculator
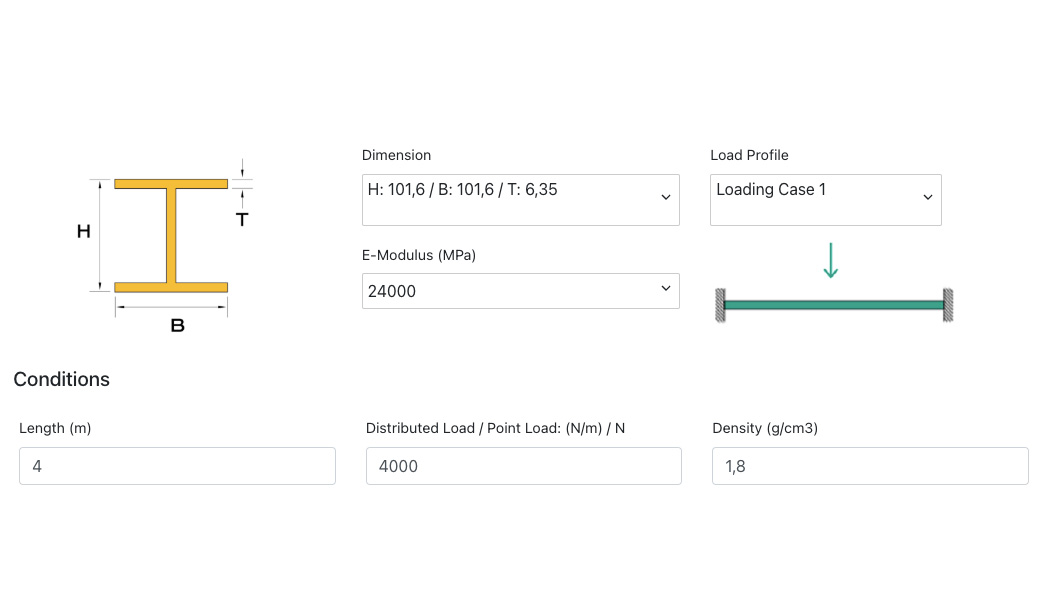
1. Profile selection
Here you select the type of profile you want to analyze.
2. Dimension
Here you select the dimensions of the selected profile type. Dimensions are given in mm as H-height, B-width and T-thickness, in the menu our available and stocked profiles are listed.
3. E-modulus (MPa)
E-Modulus(MPa) is the unit of elasticity that describes the stiffness of the profile. For our fiberglass profiles, the stiffness will be 24000 MPa.
4. Load profile
Here you choose how the load should be distributed on the profile. The following options:
– Load Case 1 – load applied in Newton (N), as a concentrated load in the middle of the profile tensioned at both ends.
– Load Case 2 – load applied evenly distributed over the entire profile in Newton per meter (N/m) on profile tensioned at both ends.
– Load Case 3 – load applied in Newton (N), as concentrated load at the end of the profile tensioned at the opposite end.
– Load Case 4 – load applied evenly distributed over the entire profile in Newtons per meter (N/m) on a profile tensioned at one end.
5.Density(g/cm3)
Density (g/cm³) is the density of the material, weight per volume. This value is pre-filled with 1.8 g/cm³ (1800 kg/m³) which applies to profiles produced by pulling the profile through a forming tool (pultrusion).
6. Length (m)
Here you enter the profile length that is exposed to load. For load cases 1 and 2, the length between attachment points / support is used. For load cases 3 and 4, the protruding length is used.
7. Distributed load (N/m) / Point Load (N)
The load to which the profile is exposed is stated here. For evenly distributed load, the load is stated in N/m (example 3,000 N/m = 3KN/m = approx. 300 kg/m). For concentrated load, the load is stated in N (example 3,000 N = 3KN = approx. 300 kg)



Results
The different results will change in real time based on the conditions you have defined above. The results give you a clear overview of how the profile behaves under load, so you can assess whether it meets the requirements of your project.
Below you will find an explanation of all the results you are presented with.

Max. Deflection (mm)
Calculated deflection in mm for the profile (maximum value). Deflection should not exceed 1 : 200 of the loaded profile length. Example: With a loaded profile length of 4,000 mm (4 m), deflection should not exceed 20 mm).
Max. Bending torque (Nm)
Bending moment for the profile in Nanometers (maximum value).
Max. Bending stress (MPa)
Bending stress for profile in Megapascal (MPa) as maximum value.
Elongation (%)
Profile elongation under load in percent.
W (mm3)
Section modulus, which describes the profile's resistance to bending.
In (mm⁴)
The moment of inertia, which describes the stiffness of the profile in bending.
Mass (kg)
Profile weight stated in kilograms.
Area (mm2)
The cross-sectional area of the profile, the area of the actual cut surface when the profile is cut crosswise.
Example
Can a 150 mm H-beam, braced at both ends, with a 4 m open span take a load of 300 kg/m (total load of 4 m = 1.2 tons)?
From the calculator, select H-profile – Under Dimensions, select H-beam with H- 152 mm, B- 152 mm, T- 6.4 mm. From the Load Profile, select Loading case 2 – evenly distributed load.
Under Length (m), enter 4 m, and under Distributed Load, enter 3000 N/m (300 kg (kp) = 2943 N).
Calculated deflection: 7 mm
The recommended maximum deflection is 1:200 which for a 4 m open span gives a maximum permissible deflection of 20 mm.
Conclusion: Calculated deflection is 7 mm. Recommended maximum deflection is 20 mm. The 150 mm H-beam can be used for a load of 300 kg/m.
Many advantages of fiberglass!
"We chose fiberglass primarily because of its longevity. There's longevity, and then there's cost of ownership."
– Jon Vestengen, General Manager
Lofoten Biomarine
